Encryption: The Cornerstone of Digital Security
Defining Encryption
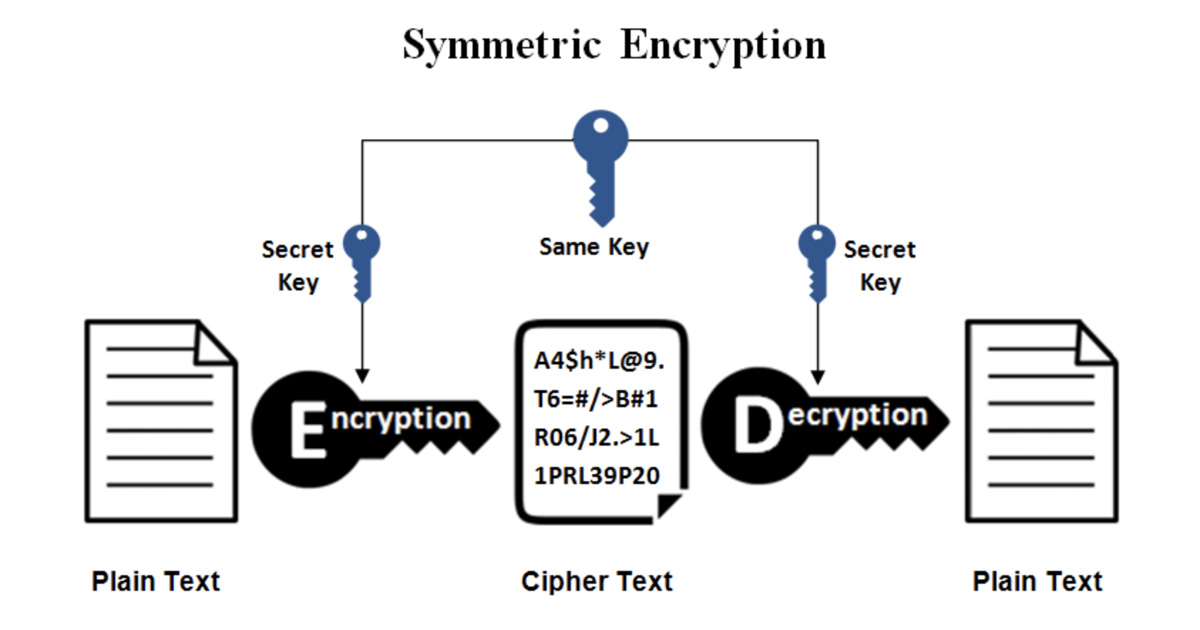
Encryption, a multifaceted concept in the world of digital security, is a process of transforming information into an unreadable format using algorithms and cryptographic keys. This transformation ensures that unauthorized individuals cannot decipher the data without the corresponding decryption key.
The Vital Role of Encryption in Digital Security
The importance of encryption in the realm of digital security cannot be overstated. It serves as the bedrock of safeguarding sensitive information in an age where data breaches and cyber threats are pervasive. Encryption acts as a shield, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data.
Historical Perspective
Origins of Encryption
The roots of encryption can be traced back to ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, who employed hieroglyphic ciphers to protect their messages. Over the centuries, encryption techniques evolved from rudimentary substitution ciphers to complex algorithms that underpin modern cryptography.
Early Encryption Techniques
Throughout history, various cultures developed their encryption methods, such as the Caesar cipher and the famous Enigma machine used during World War II. These techniques, though rudimentary by today’s standards, laid the groundwork for contemporary encryption.
Evolution of Encryption in the Digital Age
The advent of computers and the digital era led to a revolution in encryption. Traditional methods gave way to more sophisticated algorithms, and encryption became an integral part of securing data in the digital realm.
How Encryption Works

Key Concepts
Understanding encryption necessitates grasping key concepts, such as encryption algorithms, which dictate the rules for transforming data, and cryptographic keys, which are central to both locking and unlocking the encrypted data.
Encryption Process
The encryption process involves taking plain text and applying an algorithm to convert it into ciphertext, rendering it unreadable without the decryption key. This process ensures data confidentiality and privacy.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is the core application of encryption, where sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. This practice extends across various sectors, including government, finance, and healthcare.
Decryption
Decryption is the reverse process of encryption, allowing authorized users to convert ciphertext back into plain text. It requires the possession of the correct decryption key.
Encryption in Data Protection

Data at Rest
Data at rest refers to information stored on devices or in databases. To protect this data from theft or unauthorized access, encryption techniques like file and disk encryption and database encryption are employed.
File and Disk Encryption
File and disk encryption secure individual files and entire storage devices, making it challenging for malicious actors to access sensitive data even if they physically acquire the hardware.
Database Encryption
Database encryption safeguards structured data, making it an essential practice for organizations that store vast amounts of critical information. This method mitigates the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
Data in Transit
Data in transit pertains to information being transmitted over networks. To prevent eavesdropping and data interception, encryption methods like SSL/TLS for secure communication and virtual private networks (VPNs) are employed.
SSL/TLS for Secure Communication
SSL/TLS protocols create secure channels for online communication, ensuring that data exchanged between users and websites remains confidential and untampered.
VPNs and Encrypted Communication Channels
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) establish encrypted tunnels that shield data during transmission. They are instrumental in preserving privacy and security, especially in the context of remote work and online activities.
Encryption in Communication
Email Encryption
Email encryption is essential for protecting the confidentiality of email content. PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) and S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) are two widely used standards for securing email communication.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption is a powerful method ensuring that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read a message, providing a high level of security against eavesdropping.
Messaging Apps and Encryption
Popular messaging applications like Signal, WhatsApp, and Telegram implement encryption to shield the messages and files exchanged by their users from prying eyes.
The Debate on Backdoors
The debate over whether tech companies should include “backdoors” for law enforcement to bypass encryption raises crucial ethical and security questions, reflecting the ongoing tension between privacy and public safety.
Encryption in Online Banking and E-commerce
Secure Payment Transactions
E-commerce relies on secure payment transactions, with SSL certificates playing a pivotal role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of financial data.
SSL Certificates for E-commerce
SSL certificates provide the much-needed trust and security for online shoppers. These certificates encrypt payment information during online transactions, making e-commerce platforms safer for users.
Mobile Payment Apps
Mobile payment applications, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, leverage encryption to secure financial transactions on smartphones, adding convenience without sacrificing security.
Protecting Financial Data
Two-factor authentication (2FA) and end-to-end encryption are key elements in protecting financial data, adding layers of security to online banking and financial apps.
End-to-End Encryption in Financial Apps
End-to-end encryption assures that sensitive financial data is accessible only to authorized users, safeguarding personal financial information from potential threats.
Encryption in Privacy Preservation

The Role of Encryption in Privacy
Encryption plays a pivotal role in preserving individual privacy. It acts as a safeguard against unwanted intrusion and data exposure, ensuring that personal information remains confidential.
Encryption and Personal Data Protection Laws
Data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), highlight the importance of encryption in safeguarding individuals’ data rights and privacy.
Encryption in Healthcare and Telemedicine
Securing Patient Data
In the healthcare sector, securing patient data is paramount. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) compliance requires healthcare organizations to implement encryption to protect sensitive patient information.
HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA compliance mandates rigorous security measures, including encryption, to ensure that patient records remain confidential and secure.
Health Information Exchanges
Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) rely on encryption to facilitate the secure sharing of patient data among healthcare providers, ensuring efficient, yet protected, information transfer.
Encrypted Telehealth Communications
The surge in telemedicine relies on encrypted communications to protect the confidentiality of patient-doctor interactions and medical data transfer.
Challenges and Controversies
Balancing Privacy and Security
The challenge of balancing privacy and security is a complex and ongoing debate. Striking the right equilibrium is crucial to protect individual rights while maintaining public safety.
Law Enforcement Access
Law enforcement agencies seek access to encrypted data for criminal investigations, igniting a contentious debate over civil liberties, surveillance, and encryption’s role in society.
Ethical Dilemmas
Encryption presents ethical dilemmas, especially when it comes to protecting sensitive data from malicious actors while respecting individuals’ privacy rights and maintaining transparency.
Quantum Computing Threats to Encryption
The advent of quantum computing threatens contemporary encryption methods, requiring a proactive approach to adapt to this new landscape.
Post-Quantum Cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography is the vanguard of encryption research, aiming to create cryptographic algorithms that can withstand the computational power of quantum computers.
Preparing for Quantum-Safe Encryption
Preparation for quantum-safe encryption is paramount to maintain data security in a future where quantum computers may break existing encryption protocols.
Future Trends in Encryption

Advances in Encryption Technology
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital security, encryption technology continues to advance, offering new and improved methods to protect data.
Decentralized and Blockchain-Based Encryption
Decentralized and blockchain-based encryption systems are emerging as promising alternatives to centralized encryption models, offering enhanced security and transparency.
Encryption for Individuals and Businesses
Encryption Tools for Everyday Use
A plethora of encryption tools is available for everyday use, catering to individuals and businesses looking to secure their digital communications and data.
Encryption Best Practices for Organizations
For organizations, implementing encryption best practices is essential to protect sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and comply with data protection regulations.
Conclusion
In our journey through the world of encryption, we have unveiled the layers of this essential guardian of digital security. From its historical origins to its critical role in safeguarding data, encryption has proven to be an indispensable component in the realm of information protection. As we wrap up our exploration, we find ourselves not at the end, but rather at the threshold of what lies ahead.
Encryption’s Significance Unveiled
To recap, we’ve delved into the heart of encryption, understanding it as the process of transforming data into an unreadable format to thwart unauthorized access. We’ve seen how encryption, with its intricate web of encryption algorithms and cryptographic keys, stands as the bulwark against data breaches and cyber threats. It’s the technology that ensures data remains confidential, unaltered, and genuine, whether it’s at rest on a server or in transit across the vast expanse of the internet.
In the historical annals, we’ve traced the footprints of encryption, discovering that its roots stretch back to ancient civilizations. The simple substitution ciphers employed by the Egyptians, though rudimentary by today’s standards, set the stage for the complex cryptographic algorithms that underpin our modern digital world. Encryption has evolved, adopting new techniques and adapting to the challenges posed by the digital age, ultimately becoming the linchpin of digital security.
Key Concepts Explored
Our journey has also led us through the key concepts of encryption. We’ve grasped the intricacies of encryption algorithms, the mathematical underpinnings that determine how data is transformed into its unreadable form. We’ve met the dynamic duo of public and private keys, understanding how they are crucial in the encryption and decryption process, as well as how they facilitate secure communication over the internet.
In the heart of the encryption process, we’ve unveiled the intricacies of converting plain text into ciphertext, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from prying eyes. We’ve witnessed the significance of data at rest, guarded through file and disk encryption, and the secure fortresses of database encryption. Data in transit, the information coursing through networks, has found its protector in SSL/TLS protocols, and the tunnels forged by VPNs have shielded the data from eavesdropping.
Communication Fortified
Encryption’s role in communication, be it through email or messaging apps, has come under the spotlight. We’ve explored the world of email encryption, where standards like PGP and S/MIME ensure the confidentiality of electronic correspondence. End-to-end encryption in messaging apps, exemplified by Signal, WhatsApp, and Telegram, has established a new era of private communication. The debate over backdoors, aimed at balancing the needs of law enforcement with individual privacy, has underscored the ethical dilemmas encryption presents.
Online Banking and E-commerce Secured
Encryption’s footprint extends into the world of online banking and e-commerce. It is the guardian of secure payment transactions, with SSL certificates acting as the sentinels of financial data integrity. Mobile payment apps have leveraged encryption to provide users with secure and convenient financial transactions. The fortresses of two-factor authentication (2FA) and end-to-end encryption have been raised to protect financial data in the digital realm.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Encryption: The Cornerstone of Digital Security
What is encryption, and why is it important in digital security?
Encryption is the process of converting data into an unreadable format to protect it from unauthorized access. It is vital in digital security as it ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of sensitive information.
How did encryption originate, and what are its historical roots?
Encryption has ancient origins, with early techniques dating back to civilizations like the Egyptians. Over time, it has evolved from simple substitution ciphers to complex algorithms.
What are the fundamental concepts of encryption?
Key concepts in encryption include encryption algorithms, which determine how data is transformed, and public and private keys, which are essential for encryption and decryption.
Can you explain the encryption process in detail?
The encryption process involves taking plain text and applying an algorithm to convert it into ciphertext, rendering it unreadable without the corresponding decryption key.
How is data at rest protected through encryption?
Data at rest is secured through methods like file and disk encryption, which make it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access stored data.
What is the role of SSL/TLS in securing data in transit?
SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) are protocols that create secure channels for online communication, ensuring data exchanged between users and websites remains confidential and unaltered.
What are the primary encryption techniques used in communication, especially in emails and messaging apps?
Email encryption methods include PGP and S/MIME, while messaging apps like Signal, WhatsApp, and Telegram employ end-to-end encryption to protect messages and files.
What is the ongoing debate regarding encryption and backdoors?
The debate centers on whether tech companies should create “backdoors” for law enforcement to access encrypted data. It raises concerns about privacy, security, and ethical dilemmas.
How is encryption applied in online banking and e-commerce for secure payment transactions?
Encryption plays a crucial role in e-commerce, securing payment transactions through SSL certificates, which encrypt financial data during online purchases.
What are mobile payment apps, and how do they use encryption for security?
Mobile payment apps, like Apple Pay and Google Pay, utilize encryption to secure financial transactions on smartphones, providing both convenience and security.
How does encryption protect personal data and align with privacy preservation efforts?
Encryption safeguards personal data and aligns with privacy preservation by preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
What are GDPR and CCPA, and how do they relate to encryption?
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) emphasize the role of encryption in protecting individuals’ data rights and privacy.
How does encryption play a role in securing patient data in the healthcare sector?
In healthcare, encryption ensures the confidentiality of patient data and is mandated by HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) compliance.
What are Health Information Exchanges, and how do they use encryption?
Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) rely on encryption to securely share patient data among healthcare providers, ensuring efficient yet protected data transfer.
What are the challenges in balancing privacy and security with encryption?
Balancing privacy and security is challenging as it requires finding the right equilibrium between protecting individual rights and ensuring public safety.
How does encryption address the challenges posed by law enforcement access and ethical dilemmas?
Encryption is central to addressing law enforcement access and ethical dilemmas by providing security against unauthorized intrusion while respecting privacy rights.
What is the threat of quantum computing to encryption, and how is it being addressed?
Quantum computing poses a threat to existing encryption methods. Post-quantum cryptography is being developed to create encryption that can withstand the computational power of quantum computers.
What can we expect from the future of encryption?
The future of encryption holds advances in technology and innovations like decentralized and blockchain-based encryption, ensuring data security in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
In our previous chapter, we discussed the historical roots of encryption, highlighting its evolution from ancient civilizations to the complex algorithms in use today. If you’d like to delve deeper into this fascinating history, we recommend checking out the comprehensive article on “Safeguarding Your Passwords and Personal Data: Cybersecurity Tips” It provides a detailed account of encryption’s evolution, shedding light on its captivating journey through time.
For the latest insights on the future trends in encryption and the impact of quantum computing on data security, be sure to read the in-depth analysis on “Quantum Computing and Its Implications for Encryption” from Medium. This thought-provoking piece offers a thorough examination of the quantum computing threat and how the industry is gearing up for quantum-safe encryption solutions.




Uma resposta